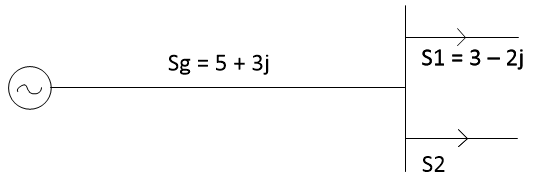Dynamic voltage restoration (DVR) is a method of overcoming voltage sags and swells that occur in electrical power distribution. Devices used for DVR include static var devices, which are series compensation devices that use voltage source converters (VSC).
The DVR is used to inject three phase voltage in series and in synchronism with the network voltages in order to compensate voltage disturbances with a benefit of active /reactive power control.