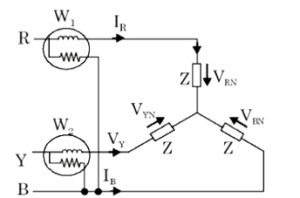
In Two wattmeter method the current coils of the wattmeter are connected with any two lines, say R and Y and the potential coil of each wattmeter is joined across the same line, the third line i.e. B as shown below in the figure . In the circuit B is the common point for both the wattmeter.