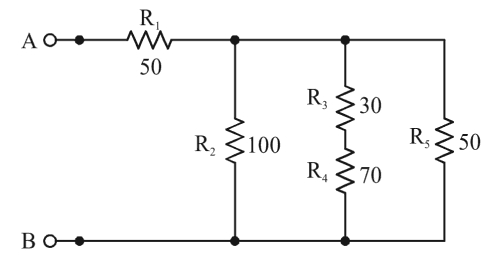
The resistance R3 & R4 are connected in series
= (30 + 70) = 100Ω
Now three resistor i.e 100Ω, 100Ω & 50Ω is connected in parallel
1/Rp = 1/100 + 1/100 + 1/50
Rp = 100/4 = 25 Ω
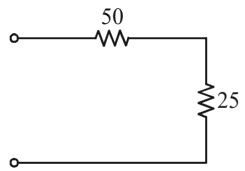
Resistance 50Ω and 25Ω are connected in series.
Rtotal = (50 + 25)Ω
Rtotal = 75Ω