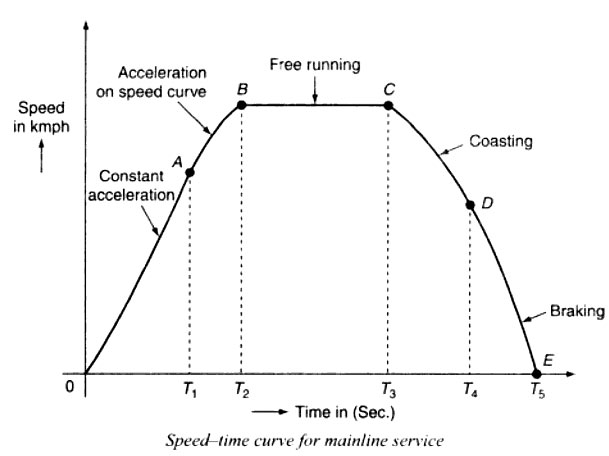
The coasting period is from T3 to T4 i.e, from C to D. At the instant, the power supply to the motor will be cut off and the speed falls on account of friction, windage resistance, etc. During this period, the train runs due to the momentum attained at that particular instant. The rate of the decrease of the speed during the coasting period is known as coasting retardation.