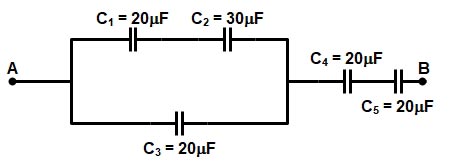
The Farad is the practical and the Sl unit of capacitance. The unit, named after Michael Faraday (1791-1867), was first suggested by Latimer Clark in 1867. The capacitor has a capacitance of 1 farad when a charge of 1 coulomb raises the potential between its plates to 1 volt.
The S.I unit of Inductance is Henry.
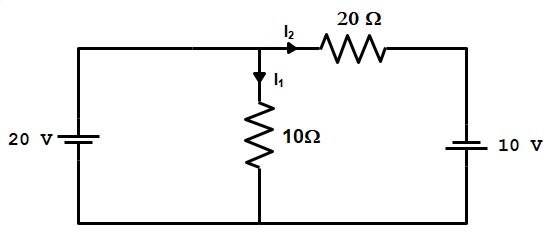
The S.I unit of resistance is OHM.
The S.I unit of Reluctance is amp-turns/Weber or Henry−1