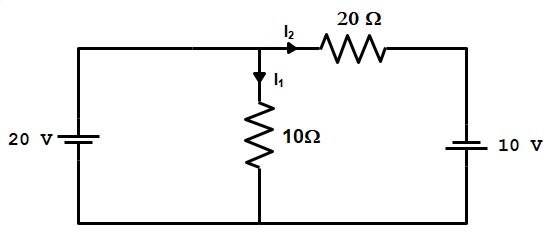
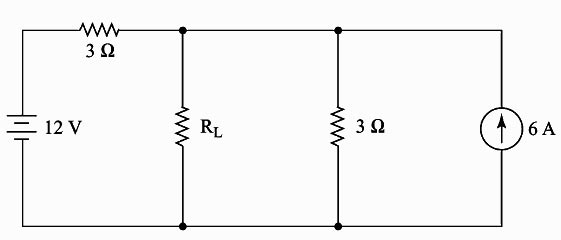
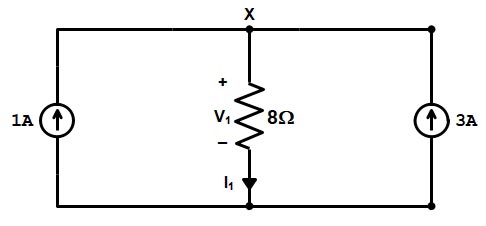
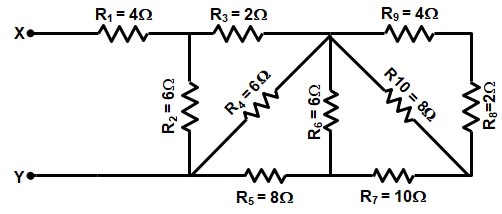
Although the Thevenin’s theorem and Norton’s theorem can be used to solve a given network, yet the circuit approach differs in the following respects:
A Norton’s theorem is converse (opposite) of Thevenin’s theorem in the respect that Norton equivalent circuit uses a current generator instead of the voltage generator and the resistance RN (which is the same as RTH) in parallel with the generator instead of being in series with it.
Thevenin’s theorem is a voltage form of an equivalent circuit whereas Norton’s theorem is a current form of an equivalent circuit.
To Convert Thevenin equivalent circuit into Norton’s equivalent circuit the following step is involved
RN = RTH
IN = ETH ⁄ RTH