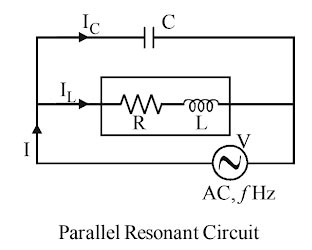
A practical parallel resonance circuit is represented by an inductance and a resistance id one branch and a capacitance in other branches.
At resonance in a practical parallel resonance circuit, the impedance is maximum. Hence, it is called a rejector circuit, and it exhibits the property of voltage magnification.
Z = L/CR